Tech Policy
We’re not going back to normal
Social distancing is here to stay for much more than a few weeks. It will upend our way of life, in some ways forever.
To
stop coronavirus we will need to radically change almost everything we
do: how we work, exercise, socialize, shop, manage our health, educate
our kids, take care of family members.
We
all want things to go back to normal quickly. But what most of us have
probably not yet realized—yet will soon—is that things won’t go back to
normal after a few weeks, or even a few months. Some things never will.
You can read all our coverage of the coronavirus/Covid-19 outbreak for free, and also sign up for our coronavirus newsletter. But please consider subscribing to support our nonprofit journalism.
It’s now widely agreed (even by Britain, finally) that every country needs to “flatten the curve”: impose social distancing
to slow the spread of the virus so that the number of people sick at
once doesn’t cause the health-care system to collapse, as it is
threatening to do in Italy right now. That means the pandemic needs to
last, at a low level, until either enough people have had Covid-19 to
leave most immune (assuming immunity lasts for years, which we don’t know) or there’s a vaccine.
How
long would that take, and how draconian do social restrictions need to
be? Yesterday President Donald Trump, announcing new guidelines such as a
10-person limit on gatherings, said that “with several weeks of focused
action, we can turn the corner and turn it quickly.” In China, six
weeks of lockdown are beginning to ease now that new cases have fallen to a trickle.
But
it won’t end there. As long as someone in the world has the virus,
breakouts can and will keep recurring without stringent controls to
contain them. In a report yesterday
(pdf), researchers at Imperial College London proposed a way of doing
this: impose more extreme social distancing measures every time
admissions to intensive care units (ICUs) start to spike, and relax them
each time admissions fall. Here’s how that looks in a graph.
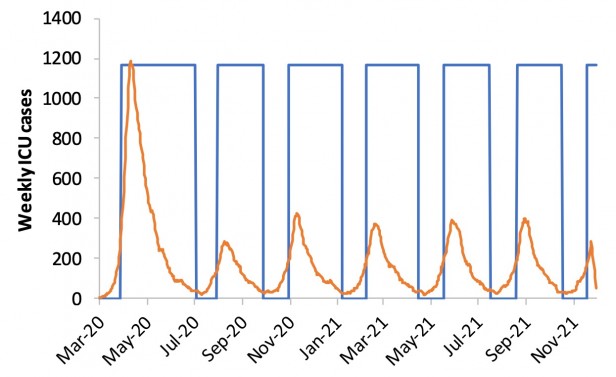
Imperial College Covid-19 Response Team.
The
orange line is ICU admissions. Each time they rise above a
threshold—say, 100 per week—the country would close all schools and most
universities and adopt social distancing. When they drop below 50,
those measures would be lifted, but people with symptoms or whose family
members have symptoms would still be confined at home.


No comments:
Post a Comment